Overview of hyaluronic acid
Chemical properties and biological characteristics of hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a polysaccharide naturally present in the human body and belongs to the class of glycosaminoglycans (GAG). Its molecular structure consists of repeated disaccharide units, which can be very long, so hyaluronic acid plays an important role in hydration and tissue support.
The molecular weight of hyaluronic acid is usually between thousands and millions of Daltons, and different molecular weights have different effects in the skin and other tissues. Large molecule hyaluronic acid is usually retained in the deep layers of the skin and provides support and structural stability to the skin; small molecule hyaluronic acid is more likely to penetrate into the surface layer of the skin, promote hydration and help activate the metabolism of skin cells.
The natural existence and role of hyaluronic acid in the skin
Hyaluronic acid is an important component of the skin, joint fluid, eyes, umbilical cord and other connective tissues. In the skin, hyaluronic acid is mainly present in the dermis and basement membrane area, as a regulator of hydration, maintaining the elasticity and firmness of the skin.
Hyaluronic acid has the following main functions:
Hydration: Hyaluronic acid has a strong water absorption capacity and can absorb and maintain about 1,000 times its own weight in water. This hydration helps maintain the plumpness and softness of the skin.
Support: As an important component of the skin matrix, hyaluronic acid can maintain the structure and firmness of the skin by interacting with other components (such as collagen and elastin).
Lubrication: In joints and eyes, hyaluronic acid can play a lubricating role, reduce friction, and protect joints and eyes from mechanical damage.
The relationship between hyaluronic acid and skin health
As we age, the content of hyaluronic acid in the skin gradually decreases. This decline is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Decreased hydration: As hyaluronic acid decreases, the hydration of the skin decreases, resulting in dryness, tightness, and even fine lines and wrinkles.
Decreased skin elasticity: The reduction of hyaluronic acid leads to a decrease in the support of the skin matrix, which affects the elasticity and firmness of the skin.
Weakened wound healing ability: Hyaluronic acid is essential for wound healing. Lack of hyaluronic acid will slow down the skin healing process and may leave scars.
Therefore, hyaluronic acid plays a very important role in skin rejuvenation treatment. By supplementing hyaluronic acid or stimulating the synthesis of hyaluronic acid in the body, the skin’s hydration, elasticity and wound healing ability can be effectively restored, while also playing a positive role in promoting the synthesis of skin collagen.
The key role of hyaluronic acid in skin wound healing
Basic process of skin wound healing
Skin wound healing is a complex biological process, which is usually divided into the following four stages:
Hemostasis: After the wound is formed, platelets aggregate and release procoagulants to form thrombi to prevent further bleeding.
Inflammatory phase: Immune cells (such as neutrophils and macrophages) are attracted to the wound area, remove infectious agents and necrotic tissue, and release proinflammatory factors to initiate the healing process.
Proliferation phase: Fibroblasts migrate to the wound site and produce extracellular matrix (such as collagen and hyaluronic acid), while new blood vessels are formed to provide oxygen and nutrients for tissue repair.
Remodeling phase: The extracellular matrix is trimmed and remodeled to form a structurally stable and functionally intact skin tissue.
Hyaluronic acid plays an important role in these stages, especially the inflammatory and proliferation phases.
The role of hyaluronic acid in the inflammatory phase
Regulating inflammatory response
In the inflammatory phase, hyaluronic acid regulates the release of inflammatory factors by binding to immune cell surface receptors (such as CD44) to avoid excessive inflammatory response.
It can reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as IL-1 and TNF-α) while promoting the production of anti-inflammatory factors (such as IL-10), thereby balancing the wound microenvironment.
Attracting immune cells
Low molecular weight hyaluronic acid (LMW-HA) can act as a chemokine to attract neutrophils and macrophages to the wound area, accelerating the removal of infectious agents and debris.
Protecting the extracellular matrix
High molecular weight hyaluronic acid (HMW-HA) covers the wound area to form a protective barrier to prevent pathogen invasion and maintain a moist environment for the tissue to promote cell function.
The role of hyaluronic acid in the proliferation phase
Promote fibroblast migration and proliferation
Hyaluronic acid binds to the CD44 receptor on the surface of fibroblasts, activates signaling pathways (such as ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways), and stimulates fibroblasts to migrate to the wound area and proliferate.
These cells are key to the synthesis of collagen and other extracellular matrix components, providing structural support for wound repair.
Stimulate angiogenesis
Hyaluronic acid promotes the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by interacting with the integrin receptors of endothelial cells, stimulating the formation of new blood vessels and providing oxygen and nutrients for wound healing.
Enhance matrix reconstruction
As an important component of the extracellular matrix, hyaluronic acid works synergistically with collagen and elastin to provide support for new tissues.
It also regulates the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), avoids excessive decomposition of the extracellular matrix, and maintains the balance of the wound repair process.
Hyaluronic acid and collagen synthesis
Basic functions and synthesis process of collagen
Collagen is the most important structural protein in the skin, accounting for about 70% of the dry weight of the dermis. It provides strength, elasticity and support functions for the skin. The synthesis of collagen is a complex process, mainly completed by fibroblasts. The synthesis process of collagen goes through the following key steps:
1. Synthesis of procollagen: Procollagen is synthesized in cells, and its structure contains key amino acids such as glycine, proline and lysine.
2. Amino acid hydroxylation: With the participation of vitamin C and iron, proline and lysine are hydroxylated to hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine, respectively. This step is crucial to the stability of collagen.
3. Formation of triple helix structure: Procollagen is further assembled into a triple helix structure and secreted into the extracellular matrix.
4. Cross-linking and maturation: Collagen forms a cross-linked network in the extracellular matrix to enhance the mechanical strength of the skin.
Hyaluronic acid supports collagen synthesis
Promotes fibroblast activity
Hyaluronic acid activates cell proliferation and secretion by binding to fibroblast surface receptors (such as CD44).
Fibroblasts produce more collagen and other extracellular matrix components with the support of hyaluronic acid.
Regulates microenvironment humidity
Hyaluronic acid has excellent moisturizing ability and provides ideal conditions for collagen synthesis by maintaining a moist environment in the dermis.
A moist environment can optimize the metabolic activity of fibroblasts and promote the production and stability of collagen.
Synergistic effect with growth factors
Hyaluronic acid can serve as a reservoir for growth factors, prolonging the action time of factors such as epidermal growth factor (EGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF).
These growth factors further stimulate collagen synthesis and enhance the skin’s regenerative capacity.
Protect collagen from degradation
Hyaluronic acid reduces collagen degradation and maintains the integrity of the skin matrix by inhibiting the excessive activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs).
Contribution of hyaluronic acid to skin moisturizing and barrier function
Hyaluronic acid's moisturizing mechanism
Hyaluronic acid is a powerful natural moisturizing factor (NMF) that can absorb and retain up to 1,000 times its own weight in water. Its moisturizing effect is achieved through the following mechanisms:
Water absorption and water retention function
The molecular structure of hyaluronic acid enables it to absorb water from the surface and deep layers of the skin to maintain skin hydration.
By forming a hydration barrier, hyaluronic acid helps reduce transepidermal water loss (TEWL).
Regulate skin moisture content
Hyaluronic acid adjusts its own moisturizing ability according to the ambient humidity, ensuring that the skin maintains appropriate moisture levels in different environments.
Hyaluronic acid supports skin barrier function
Enhances stratum corneum barrier function
Hyaluronic acid enhances the integrity and resistance of the skin barrier by synergizing with other natural moisturizing factors in the stratum corneum.
It can relieve skin problems such as dryness and desquamation, and protect the skin from external stimuli..
Reduces inflammation and irritation
Hyaluronic acid reduces redness, swelling and sensitivity caused by impaired barrier function by regulating the skin’s inflammatory response.
Repairs damaged skin
In skin with damaged barrier, hyaluronic acid promotes cell migration and proliferation, accelerating the recovery of the skin barrier.
The relationship between hyaluronic acid and skin anti-aging
Main manifestations of skin aging
Skin aging is a natural process, but external factors (such as ultraviolet rays, pollution, diet, etc.) accelerate this process. The main manifestations of skin changes during aging are:
Fine lines and wrinkles: As we age, the skin gradually loses elasticity and moisture, resulting in the appearance of fine lines, especially around the eyes, forehead, and mouth.
Skin loosening and sagging: Due to the reduction of collagen and elastin, the supporting structure of the skin weakens, causing the skin to sag and sag.
Uneven and dull skin tone: Due to ultraviolet damage and slow metabolism, skin pigmentation increases, leading to spots, age spots and other problems.
Dryness and peeling: Aging skin has reduced hydration, resulting in dry, rough skin, which may be accompanied by peeling.
Hyaluronic acid has become one of the key ingredients in anti-aging skin care through its excellent moisturizing, repairing and regenerating effects.
Hyaluronic acid's anti-aging mechanism
Replenish moisture and restore skin plumpness
As we age, the natural hyaluronic acid content in the skin decreases, resulting in a decrease in skin hydration. Hyaluronic acid can absorb and lock in a large amount of water, maintain the hydration state of the skin, reduce dryness and tightness, thereby smoothing fine lines and improving the plumpness and elasticity of the skin.
Promote collagen synthesis
Hyaluronic acid activates related signaling pathways by binding to the surface receptors of fibroblasts (such as CD44) and promoting the synthesis of collagen. Collagen is an important supporting component of the skin. Its increased synthesis helps reduce skin relaxation and sagging and restores the firmness of the skin.
Repair skin barrier
Hyaluronic acid can enhance the barrier function of the skin, reduce water loss, and prevent the invasion of harmful substances from the outside world. A healthy skin barrier helps maintain the stability of the skin and avoid environmental factors that accelerate aging.
Antioxidant effect
Hyaluronic acid itself has a certain antioxidant effect, which can neutralize free radicals, reduce oxidative damage to the skin caused by external environments such as ultraviolet rays and pollution, and slow down the aging process.
Promotes skin self-repair
Hyaluronic acid helps repair micro-damage to the skin by promoting the proliferation and migration of fibroblasts and other skin cells, accelerating the regeneration process of aging skin and improving skin texture.
Various Applications of Hyaluronic Acid
As a versatile biomolecule with excellent moisturizing and repairing properties, hyaluronic acid (HA) has been continuously applied in the medical and cosmetic fields. From topical skin care to injectable treatments, the various application forms of HA make it an important ingredient in modern dermatology and cosmetic treatments.
Topical hyaluronic acid products
1. Hyaluronic acid serum
Hyaluronic acid serum is one of the most common forms of topical hyaluronic acid. Due to the characteristics of the molecular structure of hyaluronic acid, it can form hydration on the surface of the skin, thereby increasing the moisture content of the skin and improving dry and rough skin texture. Hyaluronic acid serum usually contains a higher concentration of hyaluronic acid, which penetrates quickly and moisturizes for a long time. Through deep nourishment, hyaluronic acid serum can quickly improve skin dryness and tightness, making the skin more tender and smooth. Long-term use also helps to fade fine lines and wrinkles and slow down signs of aging.
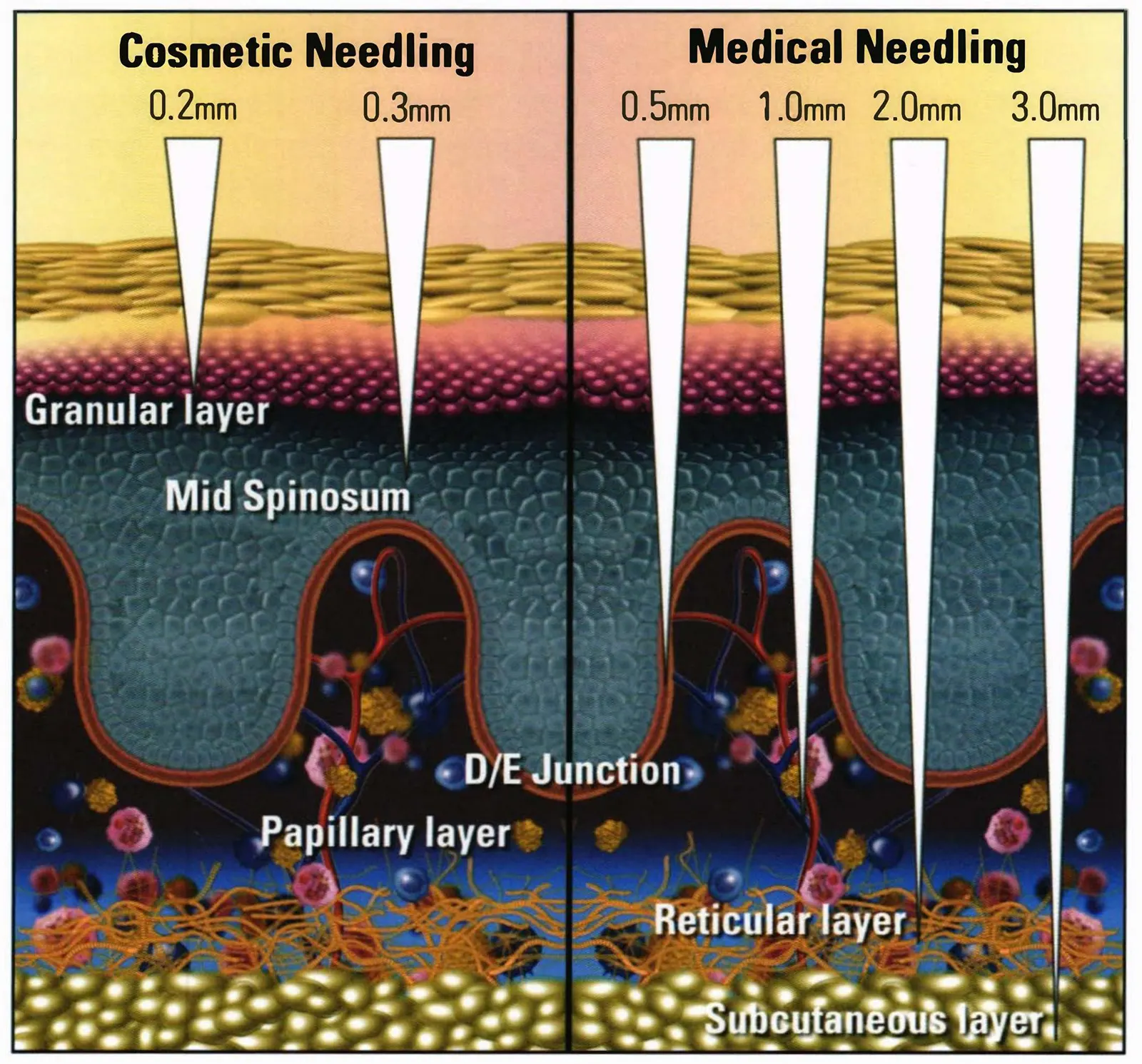
Microneedle therapy creates tiny wounds on the skin through fine needles to stimulate the skin’s repair response. Combined with hyaluronic acid serum, it can significantly improve skin hydration and promote skin self-repair and collagen synthesis.
2. Hyaluronic acid creams and lotions
Hyaluronic acid creams and lotions are products for daily skin care, usually containing lower concentrations of hyaluronic acid, mainly used to lock in moisture and maintain skin softness. These products are often used in combination with other moisturizing ingredients (such as glycerin, ceramide, etc.) to enhance the repair effect of the skin barrier. Hyaluronic acid cream is suitable for dry skin and neutral skin.
3. Hyaluronic acid mask
Hyaluronic acid mask is suitable for use when the skin feels dry or tired. It can improve the moisture and brightness of the skin in a short time. It is often used for emergency repair or special care. Hyaluronic acid mask combines hyaluronic acid with other nourishing ingredients to help intensively replenish skin moisture and restore skin elasticity and radiance.
4. Hyaluronic acid spray
Hyaluronic acid spray is a convenient external product that is often used as a hydrating artifact in daily care. It sprays hyaluronic acid and moisture directly onto the face by spraying to quickly provide moisture replenishment. It is also a convenient makeup setting product that can help keep the makeup fresh.
Hyaluronic acid injection treatment
1. Hyaluronic acid skin fillers
Hyaluronic acid skin fillers are injected into specific locations under the skin to fill wrinkles, fine lines and facial depressions. It is a common anti-aging treatment, especially effective in improving dynamic wrinkles, static wrinkles and facial contours.
Hyaluronic acid fillers are often used to improve signs of aging in areas such as nasolabial folds, nasolabial folds, and tear troughs. They can also be injected to increase the volume and fullness of the face, such as rhinoplasty and lip augmentation.
2. Hyaluronic acid joint injections
Hyaluronic acid injections are not limited to skin treatments, but are also widely used in the field of joint treatments. As a natural component of joint fluid, hyaluronic acid can help restore joint lubrication and relieve joint pain. It is often used to treat diseases such as arthritis.
3. Hyaluronic acid ophthalmic injections
The application of hyaluronic acid in the field of ophthalmology has also been gradually recognized, especially after eye surgery and in the treatment of eye diseases. Hyaluronic acid can help restore the lubrication and normal function of the eyeball.
Safety and precautions of hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a polysaccharide molecule that exists naturally in the human body and is widely found in the skin, joint fluid, eyes and other parts. Due to its natural biocompatibility and low immunogenicity, HA is widely used in the medical beauty industry and skin care field.
The topical and injectable applications of HA are generally considered safe, but in certain cases, some safety issues still need to be paid attention to.
Precautions for external use
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance in the human body that can be well accepted by the skin and other tissues. It does not cause allergic reactions when used externally, so it is relatively safe. Hyaluronic acid external products, such as creams, essences, masks, etc., are safe for most people. However, the following matters should still be noted:
1. The concentration of hyaluronic acid external products varies from brand to brand, and the common concentration range is 0.1% to 2%. For first-time users, it is recommended to start with low-concentration products to avoid irritation caused by excessive concentration.
2. For people with sensitive skin or allergies, it is recommended to choose mild hyaluronic acid products and conduct local trials to observe whether redness, swelling or allergic reactions occur within 24 hours.
3. Hyaluronic acid can be used with a variety of skin care ingredients, such as vitamin C, peptides, hyaluronic acid derivatives, etc., which can enhance its effect. However, avoid using it with highly irritating ingredients (such as strong acids and alcohols) at the same time to avoid causing dryness or irritation of the skin.
4. When using hyaluronic acid products, avoid using them with overly strong exfoliating products (such as products containing salicylic acid or fruit acid), because excessive exfoliation may damage the skin barrier and affect the moisturizing effect of hyaluronic acid.
Precautions for injection
When injected, hyaluronic acid has low immunogenicity and usually does not cause a strong reaction from the immune system. Hyaluronic acid injections (such as skin fillers) are widely used in anti-aging treatments and plastic surgery, and are relatively safe. However, the following matters should still be noted:
1. Hyaluronic acid injections should be performed in medical institutions with legal qualifications, and experienced doctors should be selected to reduce the risks during the injection process, such as overinjection, wrong location, etc. Injection operations by non-professionals may cause complications, such as vascular embolism, skin necrosis, etc., and may even affect the effect.
2. Avoid interactions with other injections. Before hyaluronic acid injections, patients should tell their doctors whether they have received injections of other skin fillers. Some fillers may interact with hyaluronic acid, affecting the treatment effect or causing adverse reactions.
3. When injecting hyaluronic acid, the appropriate injection site and depth should be selected according to different facial anatomical structures and target effects. For example, special care should be taken when injecting in sensitive areas such as the periorbital area and forehead.
4. Within 24 hours after the injection, avoid strenuous exercise, overheated environments (such as saunas, steam rooms) and excessive massage of the injection site to reduce the risk of swelling and redness.
5. Within one week after the injection, avoid direct exposure to sunlight. It is recommended to use sunscreen to protect the skin.
Ending
The various application forms of hyaluronic acid make it play an important role in the field of medical beauty and skin care. Whether it is external moisturizing care, or injectable skin filling and joint treatment, hyaluronic acid can meet the needs of different groups of people with its natural, gentle and efficient characteristics. With the continuous development of technology, the application prospects of hyaluronic acid will be broader, bringing more beauty and health benefits to consumers around the world.