In recent years, with the profound changes in the global economic landscape, the trend of regionalization and localization of supply chains has become increasingly obvious. Southeast Asian countries have become a popular destination for global manufacturing transfer with their low labor costs, superior geographical location and continuously improving investment environment. From textiles and clothing to electronic products, more and more companies are moving their production lines to Southeast Asian countries such as Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia to reduce costs and get closer to the market. However, under this trend, some industries are still firmly rooted in China, and there has been no large-scale relocation.
As an intersection of consumer electronics and personal care, the facial tools and beauty devices industry has unique market attributes and technical requirements. Unlike traditional manufacturing, this industry requires efficient production capacity and fast-response supply chains and continuous technological innovation. From simple electric facial cleansers, facial massagers to high-end beauty devices, the demand for these products in the global market, especially in Europe, the United States and Asia, continues to grow. As a major supplier, China has formed mature industrial belts in the Pearl River Delta and the Yangtze River Delta, bringing together many well-known brands and manufacturers, that not only meet production needs, but also have advantages in quality and innovation. Why is China able to maintain its leading position in this industry amid increasing cost pressures and global competition? This article will discuss this issue, analyze the advantages of this industry in China, the challenges faced by Southeast Asian countries in taking over the industrial transfer, and look forward to future development trends.
Current Status of China's Facial Tools and Beauty Devices Industry
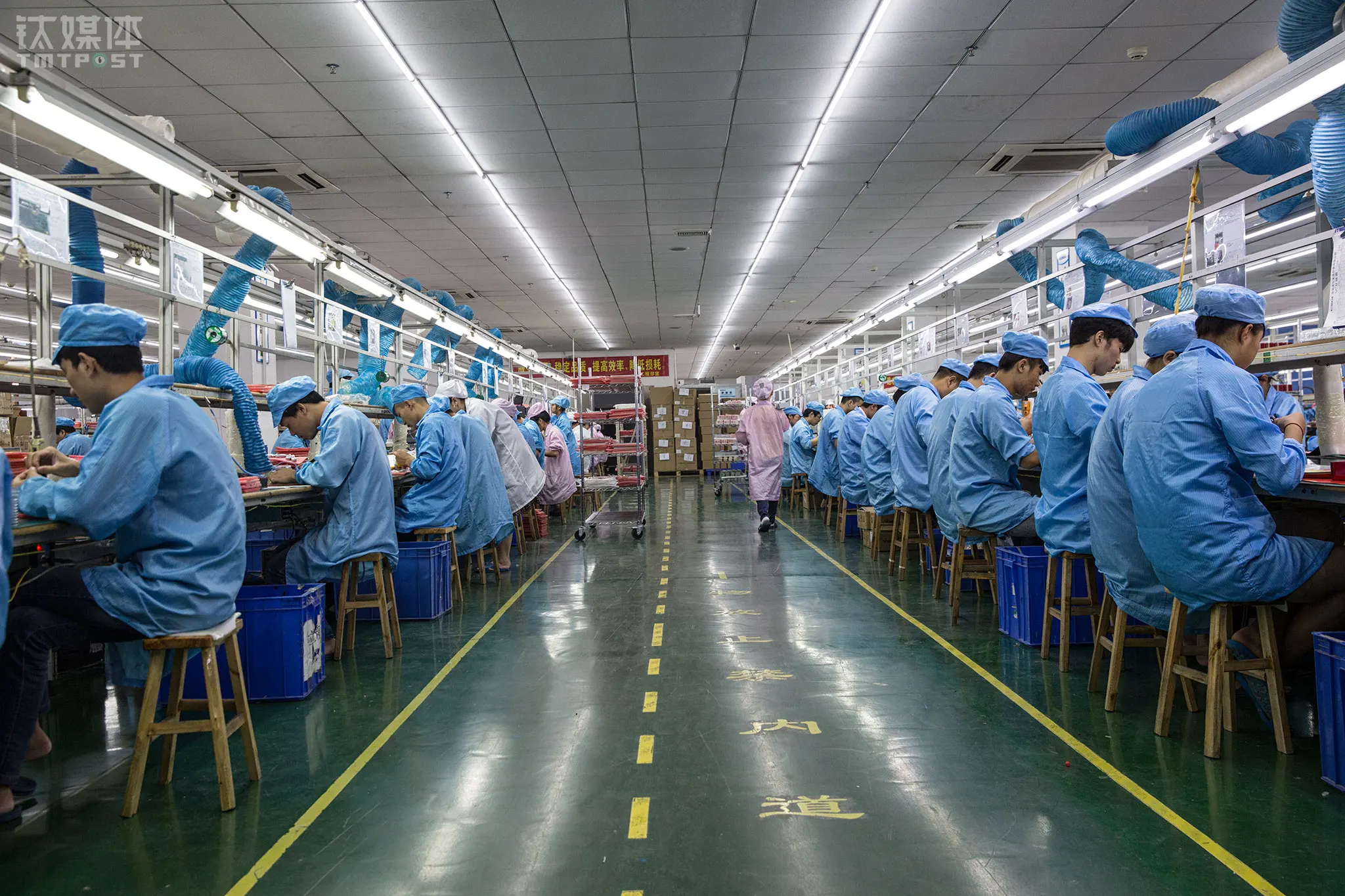
China’s facial tools and beauty devices production industry belt occupies a pivotal position in the global supply chain and its development benefits from the geographical agglomeration effect and the high integration of the industrial chain. This industry is mainly distributed in South China and East China, among which the Pearl River Delta in Guangdong, Yiwu, Wenzhou, and Ningbo in Zhejiang Province have formed significant industrial clusters.
Taking Guangdong as an example, Shenzhen, Dongguan, and Guangzhou are home to a large number of production companies, covering the entire process from R&D, design, molds, and parts manufacturing to finished product assembly; At the same time, Zhejiang is known for its small and medium-sized enterprises and flexible operating models. These regions not only have large-scale production capacity but also have formed an export-oriented industrial ecology with an annual output value of hundreds of billions of yuan.
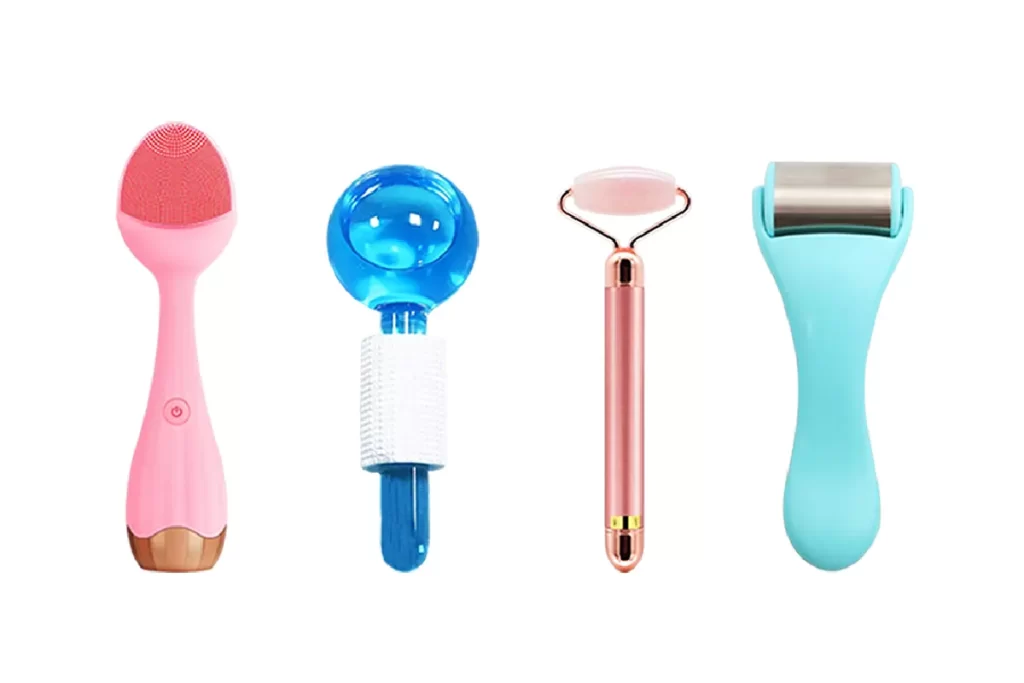
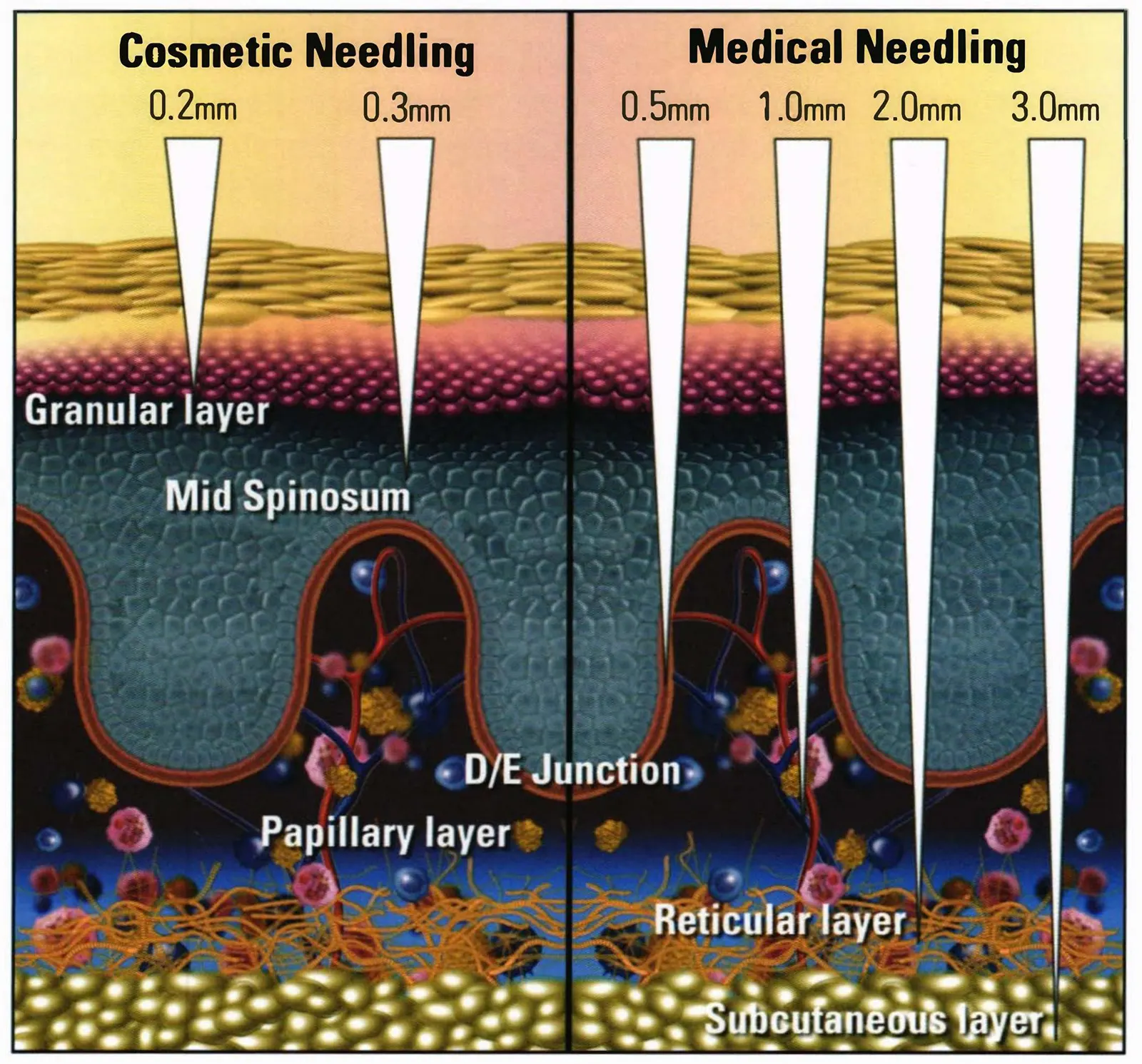
The product types of this industrial belt are rich and diverse, covering electric facial cleansers, beauty massagers for various parts of the body, photon beauty devices, microneedles, microcurrents, radio frequency beauty devices, etc. The materials involved include plastic, metal, glass, jade, silicone, wood, fiber, etc. These products include both entry-level models for the mass market and high-tech equipment for high-end consumers. In recent years, with the rise of the “face value economy” and healthy consumption concepts, the global demand for beauty devices has grown rapidly, especially in Europe, the United States, Japan, South Korea and the local Chinese market. According to industry data, facial tools and beauty devices made in China account for about 70% of the global market, showing its strong supply capacity.
The Advantages of China's Industry Belts
1. Policy Support & Improvement of Industrial Ecology
The Chinese government attaches great importance to the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry and has introduced a series of policy measures to support technological innovation and brand building. For example, tax incentives for high-tech enterprises and subsidies for R&D investment have created a good policy environment for the development of the industry. In addition, China’s perfect industrial ecology, including industry associations and exhibition platforms, provides all-round support for enterprises. China’s stable policy environment and market size provide companies with greater security and return expectations.
2. Complete & Mature Industrial Chains
Take the Pearl River Delta as an example. The industrial belts in Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan and other places have gathered a large number of upstream and downstream enterprises. From precision mold manufacturing, and electronic components supply to appearance design, packaging, and printing, all can be completed locally. This highly concentrated industrial chain layout not only reduces the production costs of enterprises, but also improves production efficiency and flexibility, and also increases the speed at which enterprises respond to market changes. Shenzhen’s electronics markets can provide the required parts within hours, but this kind of instant collaboration is still difficult to achieve in Southeast Asian countries.
3. Strong Technical Innovation Capabilities
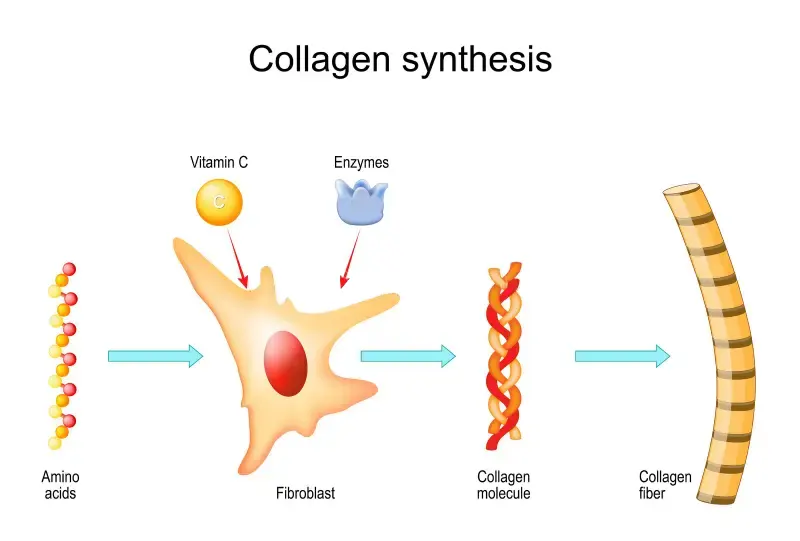
China’s facial tools and beauty device industry has strong technical accumulation and R&D strength. The Pearl River Delta has gathered a large number of high-tech enterprises and R&D talents, providing strong technical support for the industry. In recent years, domestic brands have made continuous breakthroughs in the fields of ultrasound, radio frequency, phototherapy, and microcurrent technology, launched many innovative products with independent intellectual property rights, and gradually got rid of their dependence on foreign technology.
4. A Unique Position in The Banance Between Labor Quality & Cost
Chinese workers have higher skill levels and production efficiency after long-term training. In addition, with the popularization of automation technology, the labor cost disadvantage of Chinese companies is being offset by intelligent manufacturing.
5. Efficient Logistics & Supply Chain Management
China has the most developed logistics infrastructure in the world, including ports, airports, railways, and road networks, which can ensure the efficient transportation of raw materials and finished products. In addition, domestic companies have also accumulated rich experience in supply chain management in the past few decades, which can achieve efficient coordination from production to sales, further reducing operating costs.
6. Supported by A Huge Domestic Market
China is one of the world’s largest consumer markets for beauty equipment. With the improvement of residents’ income levels and the acceleration of consumption upgrades, the domestic demand for high-quality beauty equipment continues to grow. The huge domestic market provides a broad space for development for local companies, while also attracting international brands to increase their investment in the Chinese market, further promoting the prosperity of the industry belt.
Challenges Faced by Southeast Asian Countries in Undertaking Industrial Transfer
Although Southeast Asian countries have attracted some industrial transfers in recent years due to low labor costs and preferential policies, they still face many limitations in undertaking the production supply chain of facial tools and beauty devices. These shortcomings make it difficult for them to replace China’s core position in this field.
1. Infrasture Construction Relatively Backward
Although Vietnam, Thailand and other places have increased investment in ports and roads in recent years, the coverage and efficiency of the overall transportation network are still not comparable to China. For example, many countries’ port throughput capacity is limited, and the logistics connection in inland areas is weak, resulting in long cargo transportation time and large cost fluctuations. For those products with high timeliness and fast replacement, this infrastructure shortcoming directly affects the stability of the supply chain and market competitiveness. The geographical dispersion of island countries such as Indonesia further exacerbates the complexity of logistics coordination.
2. A Significant Gap Between Technology Level & Industrial Supporting Facilities
The production of facial tools and beauty devices requires precision manufacturing technology and mature supply chain support, while the industrial base of Southeast Asian countries is still dominated by traditional manufacturing, lacking technical accumulation in the fields of microelectronics and precision molds. For example, the production of radio frequency beauty devices requires stable circuit design and high-precision component processing, which often rely on imports rather than local production in Southeast Asia. This technical dependence not only increases costs, but also prolongs the production cycle.
3. Skills & Stability of The Workforce
Although the labor costs are lower than those in China, the skill level of workers is generally low, especially when they need to operate complex equipment or engage in high-tech jobs, the training cost and time increase significantly. In addition, the labor market in Southeast Asian countries is highly mobile, and workers frequently change jobs, making it difficult for companies to maintain a stable production team. For example, in some factories in Vietnam, the worker turnover rate is as high as 20%-30%, which is a big challenge for industries that need to continuously improve processes. After decades of years of accumulation, Chinese workers have formed high professional quality and stability.
4. The Limited Market Size & Insufficient Consumption Capacity
Compared with China’s huge market, the market size of Southeast Asian countries is relatively small and the consumption capacity is limited. Although some countries such as Vietnam and Indonesia have rapid economic development, the overall consumption level is still low, which makes it difficult to support the large-scale sales of high-end beauty equipment.
5. Cultural Differences & Language Barriers
Southeast Asian countries have diverse cultures and a wide variety of languages, which brings additional challenges to the management and operation of enterprises. For example, in terms of employee training, marketing, customer service, etc., enterprises need to invest more resources to overcome cultural differences and language barriers.
6. Politics & Policy Risks
Some Southeast Asian countries have certain fluctuations in their political systems and policy stability. Changes in the political situation may lead to adjustments in policies and regulations, changes in tax policies, and changes in foreign investment policies. In additio, although many countries have introduced tax breaks and foreign investment preferential policies, their legal systems, administrative efficiency, and policy continuity are still lacking. These factors increase the risk of companies building factories in Southeast Asia, especially for industries that require long-term investment.
External Factors Strengthen China's Industry
In addition to China’s own inherent advantages, external factors have also consolidated the position of the facial tools and beauty instrument industry belt in China to a certain extent. These factors include changes in global market demand, the impact of trade policies, and the promotion of technological innovation and branding, which together provide additional support for China’s industry.
First, changes in global market demand have created space for China’s industrial belt to continue to grow.
Second, the impact of trade policies and tariffs has also objectively supported the retention of China’s industry. Although the Sino-US trade frictions in recent years have led to the relocation of some manufacturing industries, facial tools, and beauty instruments, as a relatively niche and high-tech category, have been limited by tariff impacts. At the same time, the free trade agreements signed by China with many countries (such as RCEP) provide tariff reduction advantages for its exports, further reducing the operating costs of enterprises.
Third, the promotion of technological innovation and branding has injected new vitality into China’s industry. In recent years, Chinese companies have increased their investment in technology research and development and brand building. For example, domestic brands such as ULIKE, AMIRO, etc. have launched globally competitive products through independent research and development of radio frequency and light therapy technologies.
Future Outlook And Thinking
The competitive pressure faced by China’s industrial belt cannot be ignored: with the continuous rise in labor costs and stricter environmental protection policies, some low-value-added production links may face the risk of relocation. Domestic small and medium-sized enterprises need to get rid of the inherent idea of ”low-price competition”, focus on brand building and user experience, create influential high-end brands, and increase product added value. Therefore, maintaining a balance between cost advantage and technological leadership will become a key challenge for future development.
In general, the future development of China’s facial tools and beauty devices industry belt will move forward amid opportunities and challenges. In the short term, its comprehensive advantages are still difficult to be replaced; but in the long run, only through technological upgrading and strategic adjustments can it continue to lead in the global supply chain competition. In addition, China and Southeast Asian countries are not simply in a competitive relationship in the field of facial tools and beauty instruments, but can explore a new model of win-win cooperation, use their respective advantages to achieve optimal resource allocation, and jointly promote the development of the industry.
Wholesale and Custom Facial Tools & Beauty Devices
ROSEORCHID focuses on facial tools and the beauty device industry, the main products include ice globes, ice rollers, microneedles, facial massagers, (including neck beauty massagers, electric gua sha, etc), body massagers, photon beauty devices, and other beauty device products. All products are produced in high-quality industrial belts in the Pearl River Delta and Yangtze River Delta regions to ensure high-quality and efficient supply.
With decades of industry experience, we strictly select to ensure that each product is cost-effective and market-competitive. We provide wholesale and customized services to meet the needs of different customers. In addition, we also have a complete packaging design and transportation supply chain, providing you with a one-stop solution from production to delivery, ensuring that you enjoy an efficient and reliable service experience.